ISC 11>Content>Unit-4>Biomolecules
Scope of syllabus
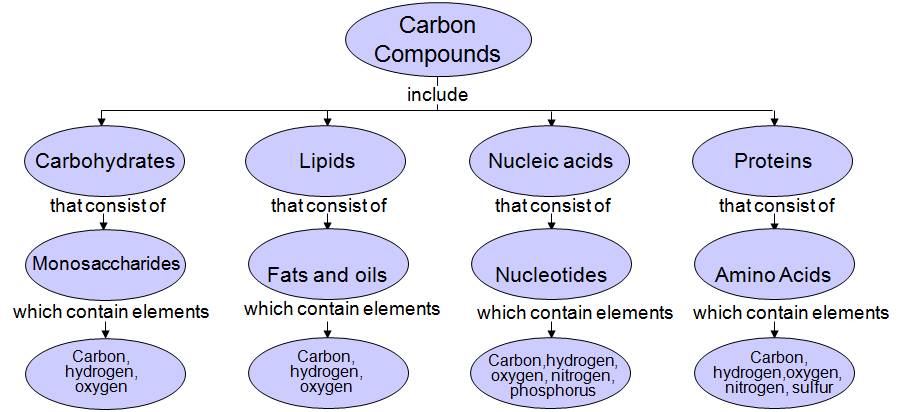
Biomolecules:
- Carbohydrates- General classification and functions of: monosaccharides (glucose, ribose and deoxyribose), disaccharides (maltose, lactose and sucrose), polysaccharides (glycogen, starch, cellulose, inulin, and chitin).
- Proteins- Amino acids – (structure: glycine, alanine, serine); amino acids as zwitter-ion; examples of acidic, basic, neutral, sulphur containing amino acids; essential and nonessential amino acids; levels of protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary); functions of proteins.
- Lipids – classification, structure and functions of fats and oils
- Nucleotides and nucleic acids – structure and functions of DNA, types of RNA. Differences between DNA and RNA
Biomolecules
The molecules occurring in living organisms are called biological molecules.
The molecules occurring in living organisms are called biological molecules.
Basics of biochemistry
|
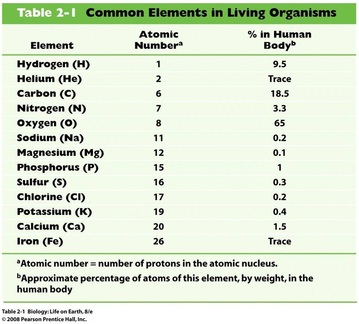
A. Common elements
|
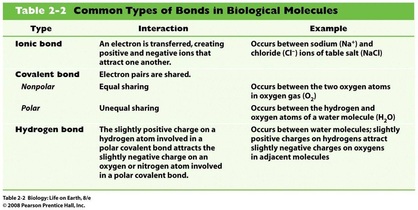
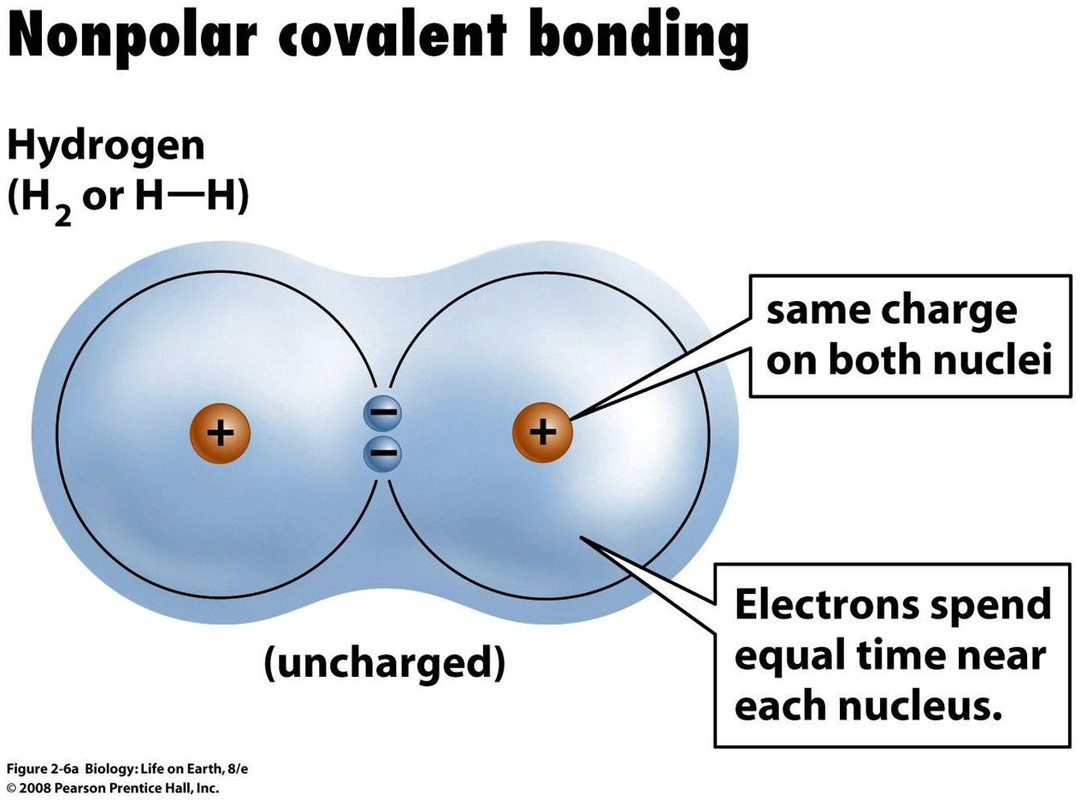
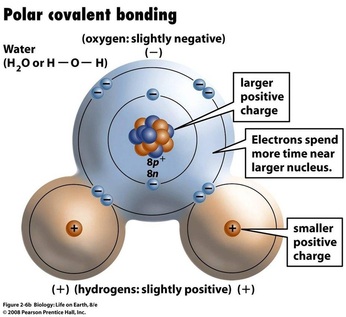
3. Polarity: Electrons in a covalent bond may be equally or unequally shared between the atoms
4. Carbon
Why Is Carbon So Important?
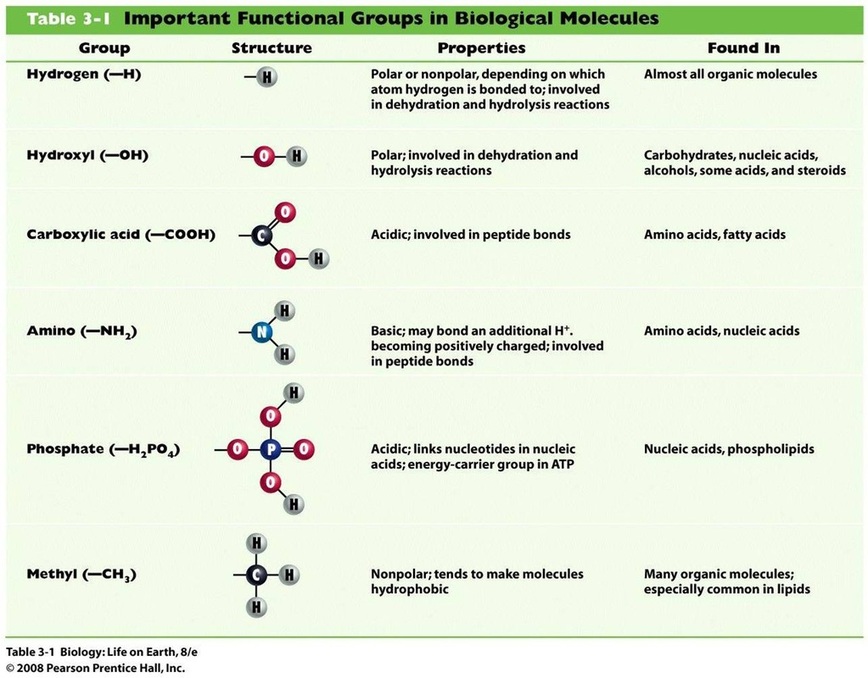
- Carbon atoms are versatile and can form up to four bonds (single, double, or triple) and rings..
- Functional groups in organic molecules confer chemical reactivity and other characteristics.
- Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules
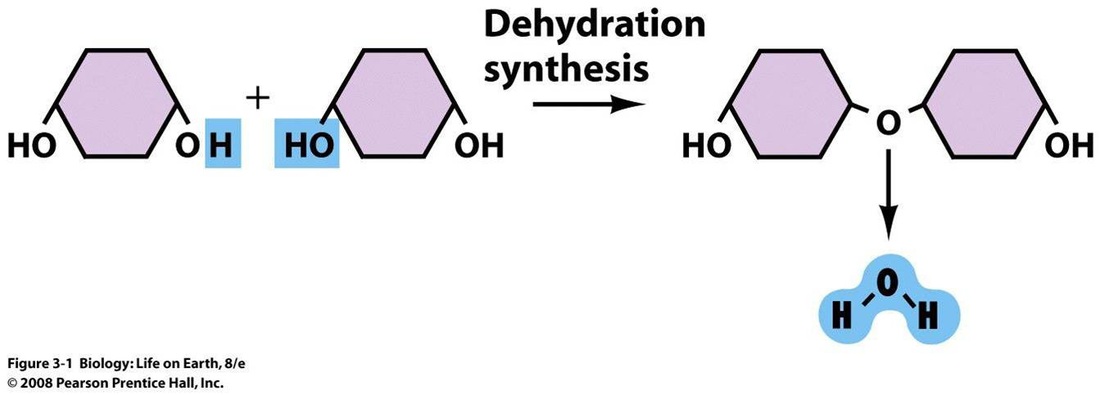
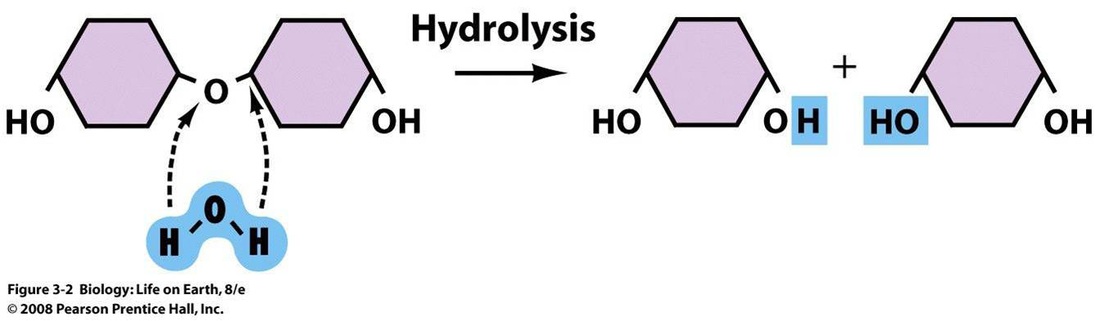
5. Condensation and hydrolysis
Condensation: A chemical reaction in which two molecules combines to form single molecule, with the loss of a small molecule (Water)
Hydrolysis: A reaction in which water is used to split a substance into smaller particles.
Condensation: A chemical reaction in which two molecules combines to form single molecule, with the loss of a small molecule (Water)
Hydrolysis: A reaction in which water is used to split a substance into smaller particles.
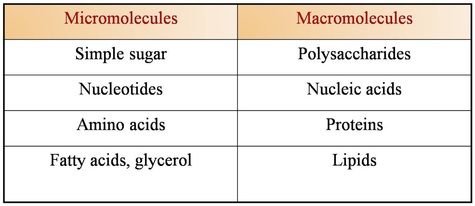
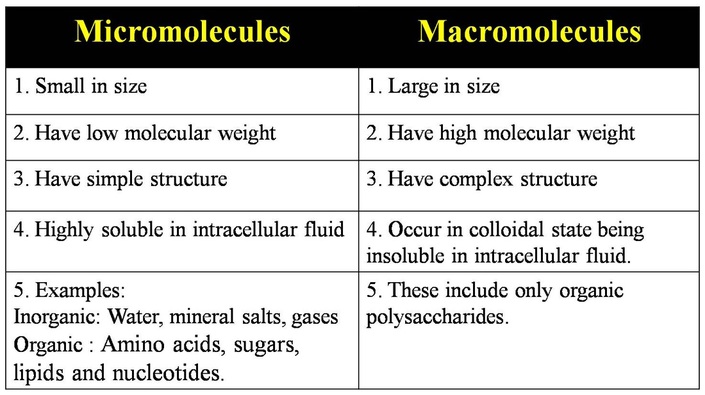
Micromolecules and macromolecules