ICSE 10> HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY> 9.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Scope of syllabusEndocrine System: General study of the following glands: Adrenal, Pancreas, Thyroid and Pituitary. Difference in Endocrine and Exocrine glands.
Correct location and shape of the gland in the human body should be discussed along with the hormones they secrete (Pancreas: insulin and glucagon to be taught; Thyroid: only thyroxin to be taught). Effects of hypo secretion and hyper secretion of hormones must be discussed. The term tropic hormones should be explained in the study of pituitary. Brief idea of feedback mechanism must be given. |
Class Presentation |
Types of glands
|
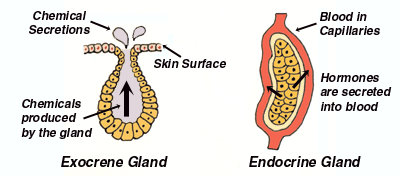
Human body has two types of glands based on the presence of ducts-
|
|
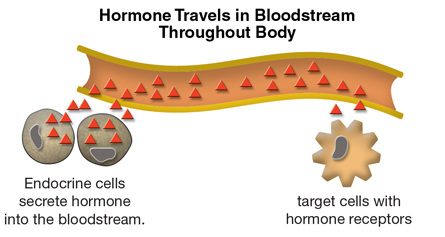
Endocrine glands release hormones in the blood stream, that travels throughout the body and reach the target cell.
Hormones-
|
http://resource.rockyview.ab.ca/t4t/bio30/images/m2/b30_m2_021_l.jpg
|
|
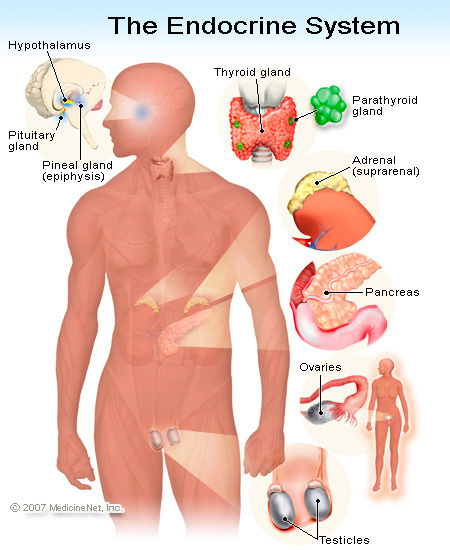
list of endocrine glands- |
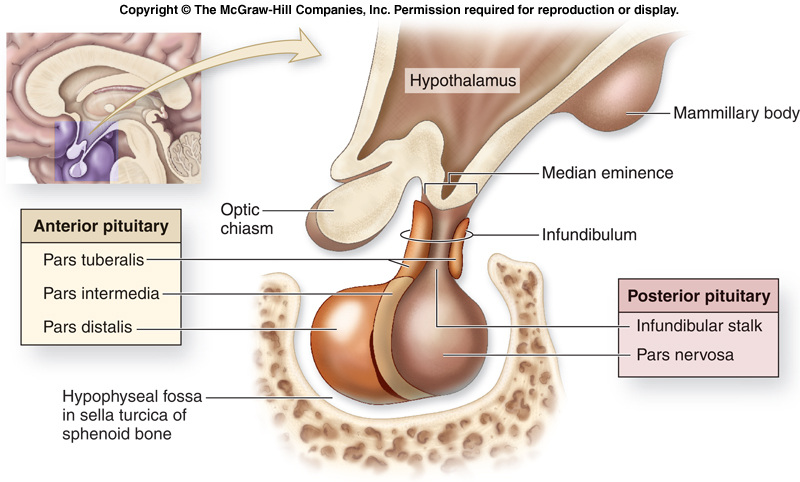
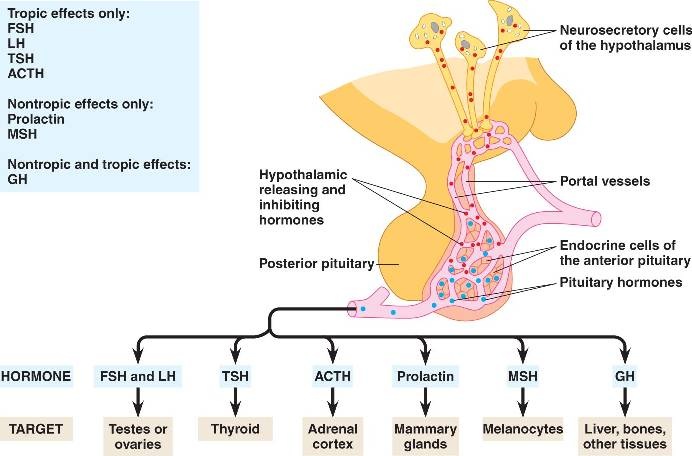
Pituitary gland
|
Location- in the brain attached to hypothalamus
Pear shaped Divided into three lobes –
Pituitary is connected to the hypothalamus by a stalk called INFUNDIBULUM. It is connected by the hypothalamo-hypophysial portal system and axons of hypothalamic neurons. |
Anterior pituitary
|
Tropic hormones- These are hormones that activate other endocrine glands to release their hormones or act on target organs.
Non tropic hormone-
|
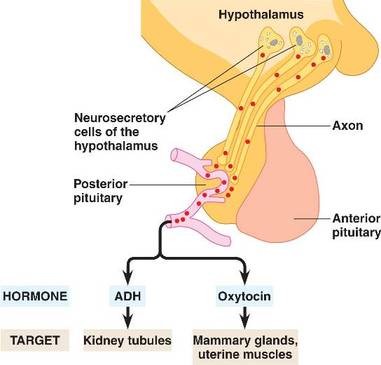
Posterior pituitary
|
Posterior pituitary is an extension of the hypothalamus connected by nerve fibers.
It does not secrete any hormone, it stores and releases the hormones secreted by the hypothalamus. The hormones released by posterior pituitary are- 1. Anti-diuretic hormone or vasopressin. It stimulates re-absorption of water from the kidneys and increases blood pressure by acting as a vasoconstrictor. 2. Oxytocin or pitocin. It stimulates contraction of uterine muscles during child birth and milk ejection from mammary glands. |
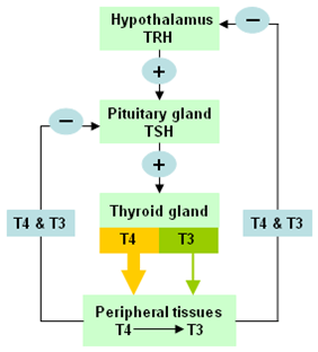
How are the hormone levels regulated?
|
Feedback mechanism
The endocrine hormones are regulated by feedback mechanism. The hormones released by the target gland regulates its further production. This effect may be positive or negative. In positive feedback the endproduct stimulates the secretion of the releasing factor. In negative feedback the endproduct inhibits the secretion of the releasing factors. The feedback mechanism can be- By hormones- when the increase or decrease in the target gland hormone acts as inhibitor or stimulator respectively. By metabolites- the blood metabolite level control the hormone release. By nervous control- Adrenal medulla hormones are controlled by the sympathetic nervous sytem. |
Somatotrophic hormone or Somatotrophin or growth hormone
It is secreted by the anterior pituitary.
It is secreted by the anterior pituitary.
- Stimulates body growth by stimulating mitosis.
- Stimulates retention of proteins and calcium in the body.
- Helps in growth of long bones.
|
Hyposecretion of STH (hGH)
Decrease in secretion during childhood. Causes dwarfism- stunted growth of bones and other body organs. |
Hypersecretion of STH (hGH)
Oversecretion from childhood Causes gigantism - abnormal elongation of all bones, produces giant size persons called pituitary giants. Over secretion of GH after adolescence, causes acromegaly. They are called disproportionate giants, elongation of certain body parts like hands, feet and jaws. |
Vassopressin or Antidiuretic hormone
It acts on the kidney and stimulates reabsorption of water, thereby reducing the loss of water through urine.
It also causes narrowing of arteries acting as a vasoconstrictor.Hyposecretion causes Diabetes insipidus.
Large amounts of urine excreted, dehydration and thirst.
It acts on the kidney and stimulates reabsorption of water, thereby reducing the loss of water through urine.
It also causes narrowing of arteries acting as a vasoconstrictor.Hyposecretion causes Diabetes insipidus.
Large amounts of urine excreted, dehydration and thirst.
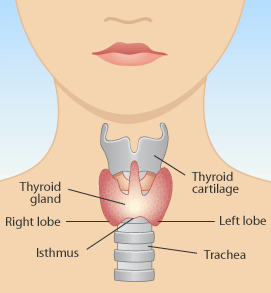
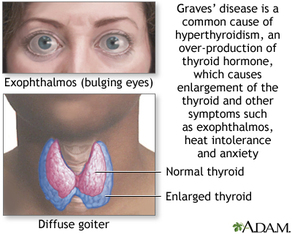
THYROID GLAND
|
It is a butterfly shaped gland, consisting of two lobes connected by a strip of connective tissue - isthmus
Location- Either side of the trachea, in front of larynx. The thyroid secretes two main hormones- Thyroxine Triiodothyronine Functions of the hormone- Regulate the basal metabolic rate (BMR). Essential for normal development of brain and mental alertness. They also promote normal skeletal growth. |
Hypothyroidism
|
1. Cretinism in children
Retarded mental & physical growth Immature sexuality &retarded sexual characters |
2. Myxoedema or Gull’s disease in adults
Low BMR, body temperature & BP Mental, physical dullness & loss of memory Degenerated sex organs |
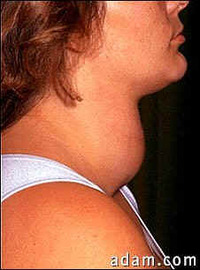
3. Simple Goitre
Enlargement of thyroid due to deficiency of iodine in food. |
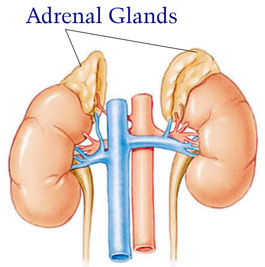
Adrenal glands
|
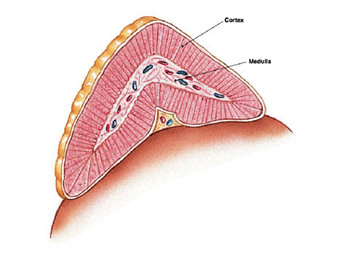
Hormones of adrenal cortex:
1. Glucocorticoids •Cortisol- metabolism of carbohydrates, fats &protein •Construction of blood vessels during excessive bleeding 2. Mineralocorticoids •Metabolism of Na & K & water balance. •Aldosterone reduces removal of Na but increases K elimination •Retention of Na in blood increases absorption of water & increases blood vol. 3. Sex steroids •Proper functioning of sex organs & development of sex character. •Androgens and estrogens |
|
Hyposecretion of cortisol & aldosterone
•Causes Addison’s disease •Bronze like pigmentation of skin •Muscular weakness, low BP, low blood sugar, odema, nausea, insomnia, diarrhea etc. |
Hypersecretion:
Excessive cortisol •Cushing’s syndrome •Excessive deposition of fat on face (obesity) •In males –hirsutism-excessive body hair growth In female- masculinisation-growth of beard, moustache etc. Excessive aldosterone •Aldosteronism/Conn’s syndrome •High plasma Na, low K+ •Increase blood volume & BP, muscular weakness •polyuria (excessive urination) Excessive adrenal androgens •Adrenal virilism / adreno-gential syndrome •Reversal of sex characters in adults •Female tend change to males uterus & ovaries degenerate. |
Hormones of the adrenal medulla
Two hormones:
1.Non Adrenaline- (Non Epinephrine)
•Regulates BP, transmits nerve impulse
2. Adrenalin (Epinephrine)
•Secreted during emergency like emotional stress, anger, fear & grief.
•Vasoconstrictor
•Carbohydrate metabolism
•Bronchodilating treatment of Asthma
Two hormones:
1.Non Adrenaline- (Non Epinephrine)
•Regulates BP, transmits nerve impulse
2. Adrenalin (Epinephrine)
•Secreted during emergency like emotional stress, anger, fear & grief.
•Vasoconstrictor
•Carbohydrate metabolism
•Bronchodilating treatment of Asthma
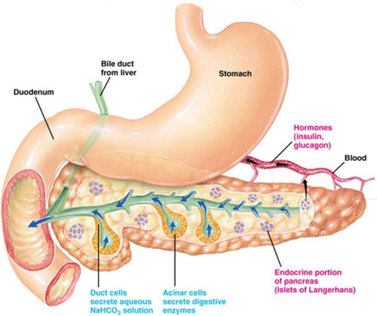
The Pancreas
|
pancreas is an oblong flattened gland located deep in the abdomen sandwiched between the stomach and the spine The pancreas is made up of glandular tissue and a system of ducts
The endocrine (endo= within) cells of the pancreas produce and secrete hormones into the bloodstream. The pancreatic hormones, insulin and glucagon, work together to maintain the proper level of sugar in the blood. This part is called islets of Langerhans. Secretes two hormones 1.Insulin (beta cells) –Lowers blood glucose –Induces protein synthesis –Induces synthesis of enzymes converting glucose – glycogen – Deficiency •Diabetes mellitus •Hyperglycemia •Diuresis 2.Glucagon (alpha cells) –changes liver glycogen-glucose –forms glucose from amino acid –increases blood glucose level |
|
Diabetes mellitus
Caused due to decrease in insulin levels. Results in hyperglycemia |
Diabetes insipidus
caused due to decrease in ADH levels results in excess urination |
|
|
|
|