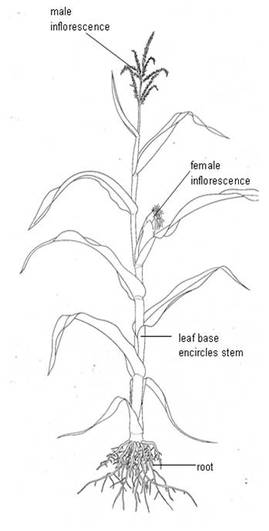
ISC-12>PRACTICAL>OBSERVATION>PLANT MORPHOLOGY
I. STUDY OF INFLORESCENCE
AIM:Identification, drawing and comments on inflorescence
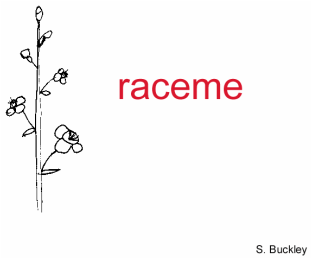
A. RACEMOSE INFLORESCENCE
EXAMPLES OF RACEMOSE
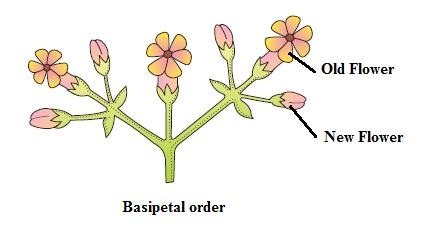
B. CYMOSE INFLORESCENCE
EXAMPLES OF CYMOSE
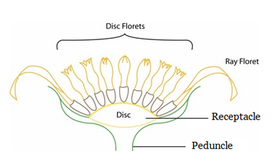
C. CAPITULUM
|
II. ADAPTATION TO POLLINATION
AIM: To study the flowers adapted to pollination by different agencies.
- Flowers adapted to pollination by different agencies.
- Students should be able to identify the type of pollination of the given flower, draw the diagram of the flower and give two reasons for the type of pollination.
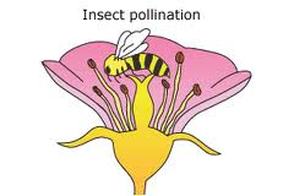
A) Insect pollinated flower :
Comments :
- Petals: Present, often large, coloured and scented.
- Nectar: Produced by nectaries to attract insects
- Stamen: Present inside the flower
- Pollen: Smaller amount , often round, sticky or have projection to attach to furry bodies of insects.
- Stigma: Small surface area, inside the flower
- Examples: Rose, sunflower etc
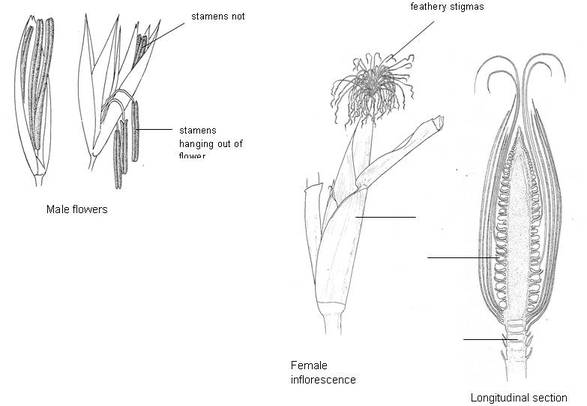
B) Wind pollinated flower :
Comments
- Flowers inconspicuous, non showy and not brightly coloured.
- Flowers are devoid of scent and nectar.
- Stamens are pendulous and also hang outside the flower.
- Anthers are versatile i.e. they are attached at the midpoint, so they will swing freely in the wind.
- Pollen are produced in large number.
- Stigmas are large, branched and feathery – and held outside the flower