ISC-12>PRACTICAL>TAXONOMY
STUDY OF FLORAL CHARACTERISTICS THROUGH FLOWER DISSECTION
A. AIM: To study the floral characteristics of family Malvaceae by dissection of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis
- Inflorescence: Solitary axillary
- Floral characteristics:
|
Epicalyx:
Stamen
Carpel
Style- Long, united below, free above, passes through staminal tube Stigma-Five in number, capitate Placentation-Axile |
|
Characteristic of the family:
|
Economically important plants:
Edible plants:
|
B. AIM: To study the floral characteristics of family Solanaceae by dissection of Datura stramonium
- Inflorescence :Solitary axillary
- Flower: Ebracteate, Pedicellate,complete, bisexual/hermaphrodite, actinomorphic, hypogynous, pentamerous, cyclic.
|
Calyx:
Stamen
Carpels
Style: Long Stigma: Slightly bilobed Placentation : Axile with swollen placenta/ obliquely placed placenta |
|
Characters of the family solanaceae
|
Economically important plants:
They provide several important food and medicinal plants.
|
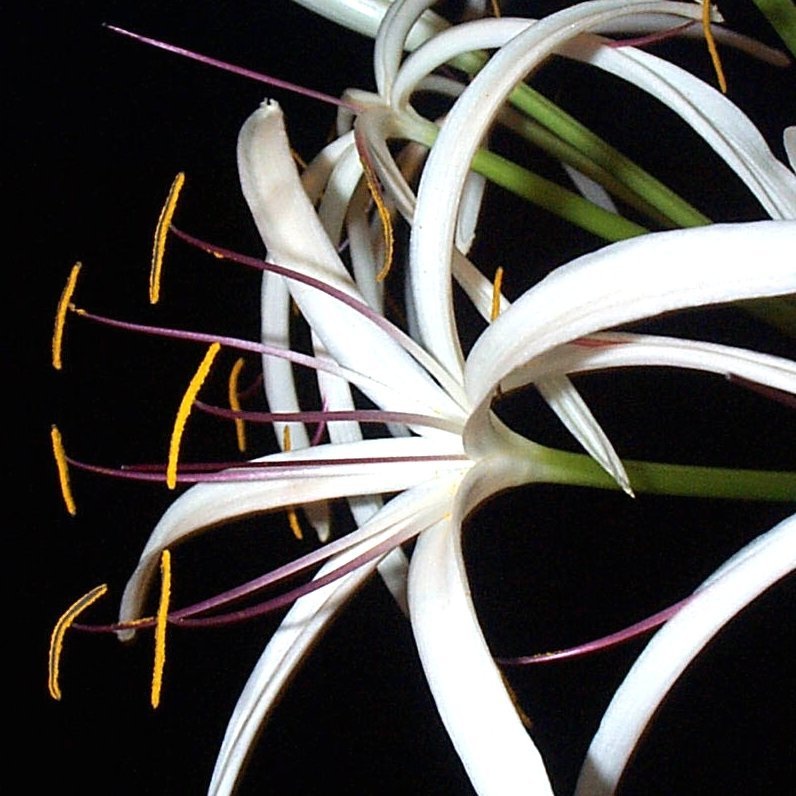
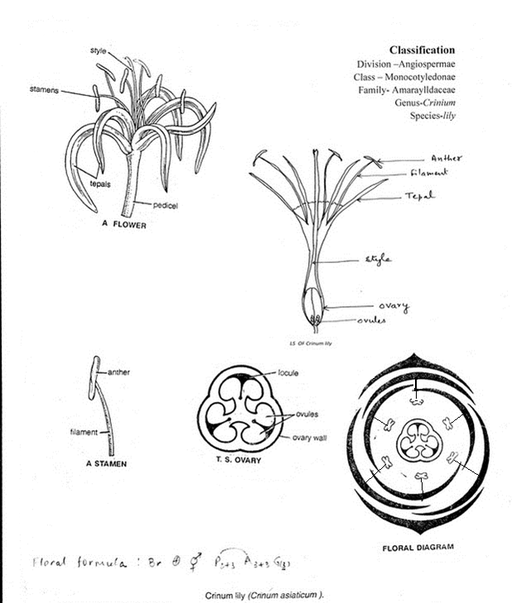
C. AIM: To study the floral characteristics of family Amaraylldaceae by dissection of Crinium lily.
- Inflorescence: Umbel
- Flower: Bracteate, pedicellate, complete, actinomorphic, hermaphrodite, trimerous, epigynous.
Carpel
Stigma: Minute Placentation: Axile |
|
Characters of the family
|
Economically important plants:
|
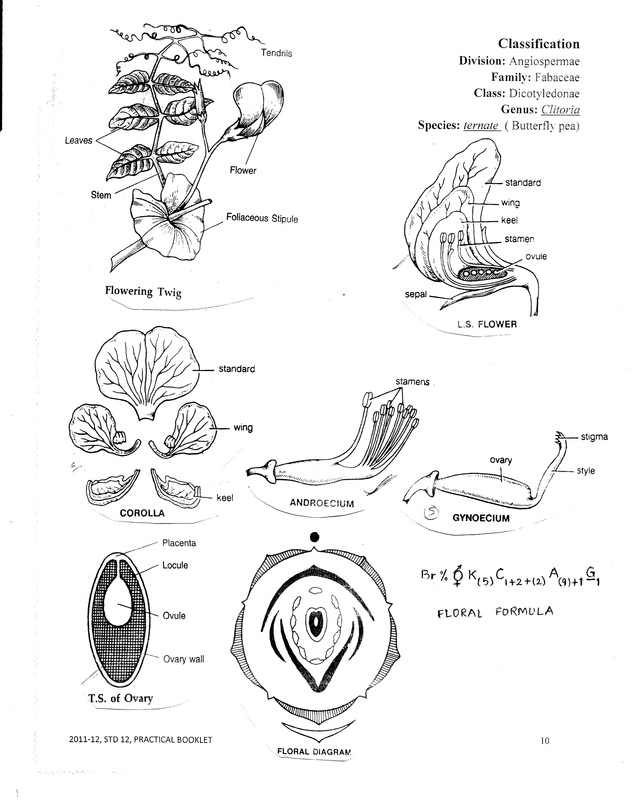
D. AIM: To study the floral characteristics of family Fabaceae/ Leguminosae by dissection of Clitoria ternate.
- Inflorescence: Racemose type
- Flower -Complete, pedicellate, bracteate, hermaphrodite, zygomorphic, hypogynous, pentamerous, papilionaceous.
|
Calyx:
Androecium: Stamen
Carpel
Style- Long and curved Stigma- Flattened or feathery Placentation- Marginal |
|
Characters of family leguminosae
|
Economically important plants:
|
CURRENTLY NOT IN SYLLABUS
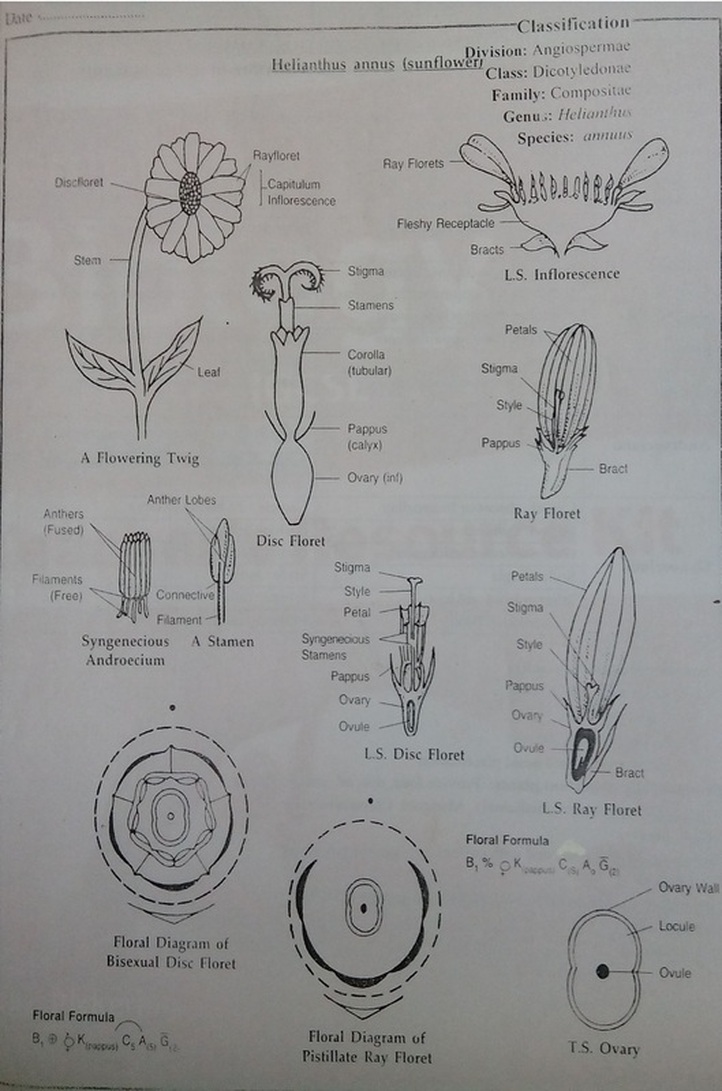
E. AIM: To study the floral characteristics of Family Asteraceae/Compositae through dissection of flower Helianthus annuus.
Inflorescence: Capitulum, with involucres. It consists of two types of flowers:
a) Ray florets (ligulate type) and
b) Disc florets tubular type.
Flowers:
a) Ray florets (ligulate type) and
b) Disc florets tubular type.
Flowers:
|
RAY FLORETS
Position: Arranged on the periphery of capitulum Flower (Floral characters): Bracteate, sessile, incomplete, pentamerous, zygomorphic, ligulate, pistillate, irregular, epigynous. Calyx: Absent or 3 and modified into pap pus. Corolla: Petals 5, gamopetalous, having a short basal tube. Androecium:Absent. Gynoecium: Carpel: absent or bicarpellary Fusion: Syncarpous Ovary: inferior, unilocular Style: single Stigma: Bifid and hairy Placentation: Basal DISC FLORETS Position: Arranged in the central part of the capitulum. Flower (Floral characters): Bracteate, sessile, complete, tubular, actinomorphic, pentamerous bisexual and epigynous. Calyx: Reduced and modified into 2-3 scales called pappus. Corolla: Petals 5, gamopetalous and tubular, valvate aestivation. Androecium: Stamens - 5, syngenesious, epipetalous, Anthers - dithecous, bilobed, basifixed, introrse. Gynoecium: Carpels: 2 (bicarpellary) Fusion: Syncarpous Ovary: inferior, unilocular Style: long Stigma: Bifid Placentation: Basal |
|
Characteristics of the family:
|
Economically important plants: Provide food, dye, oil and medicines.
Calendula officinalis (medicinal), Marigold, Chrysanthemum Edible plants: Cichorium intybus (blended with coffee), Helianthus tuberosus Oil yielding: Carthamus tinctorius (safflower), Helianthus annuus (sun flower) Ornamental: Dahlia pinnata |
OR
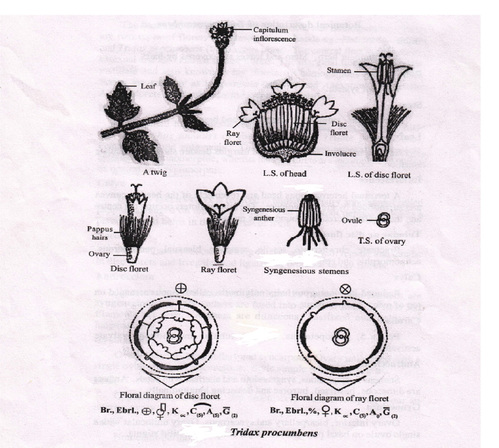
AIM: To study the floral characteristics of family Asteraceae/Compositae.
|
Inflorescence- Head or capitulum type of inflorescence.
TUBULAR OR DISC FLORETS
Stamens
Carpel-Bicarpellary, unilocular Ovary Inferior, and syncarpous. Style-simple Stigma-bifid Placentation-basal. |
LIGULATE OR RAY FLORETS
Bracteate, ebracteolate, sessile, incomplete, pistillate, zygomorphic and epigynous.
Calyx
Ovary-Inferior, unilocular
Placentation-Basal.
Style -Simple
Stigma- Bifid.
Bracteate, ebracteolate, sessile, incomplete, pistillate, zygomorphic and epigynous.
Calyx
- Number- Numerous, reduced into hairy outgrowths called pappus arranged on top of the ovary and persistent.
- Number- 5
- Fusion- gamopetalous, irregular, ligulate or bilabiate, the anterior lip is large and 3 lobed, the posterior one is small in the form of 2 teeth like projections
- Aestivation - valvate.
- Absent.
Ovary-Inferior, unilocular
Placentation-Basal.
Style -Simple
Stigma- Bifid.