ISC 12> STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF ANIMALS>DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
DISEASES RELATED TO DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
The inflammation of the intestinal tract maybe caused due to bacterial or viral infections, it can also be caused by the parasites of the intestine like tapeworm, roundworm, threadworm, hookworm, pin worm, etc.
JAUNDICE
|
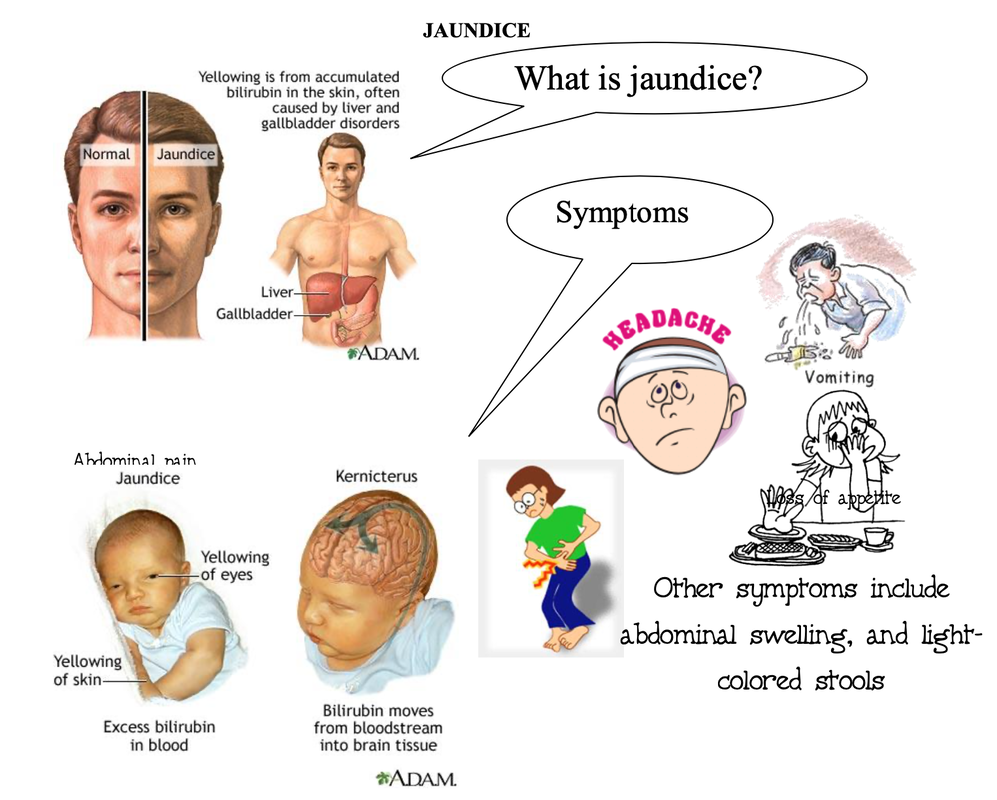
Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes caused by an accumulation of a cellular waste production called bilirubin.
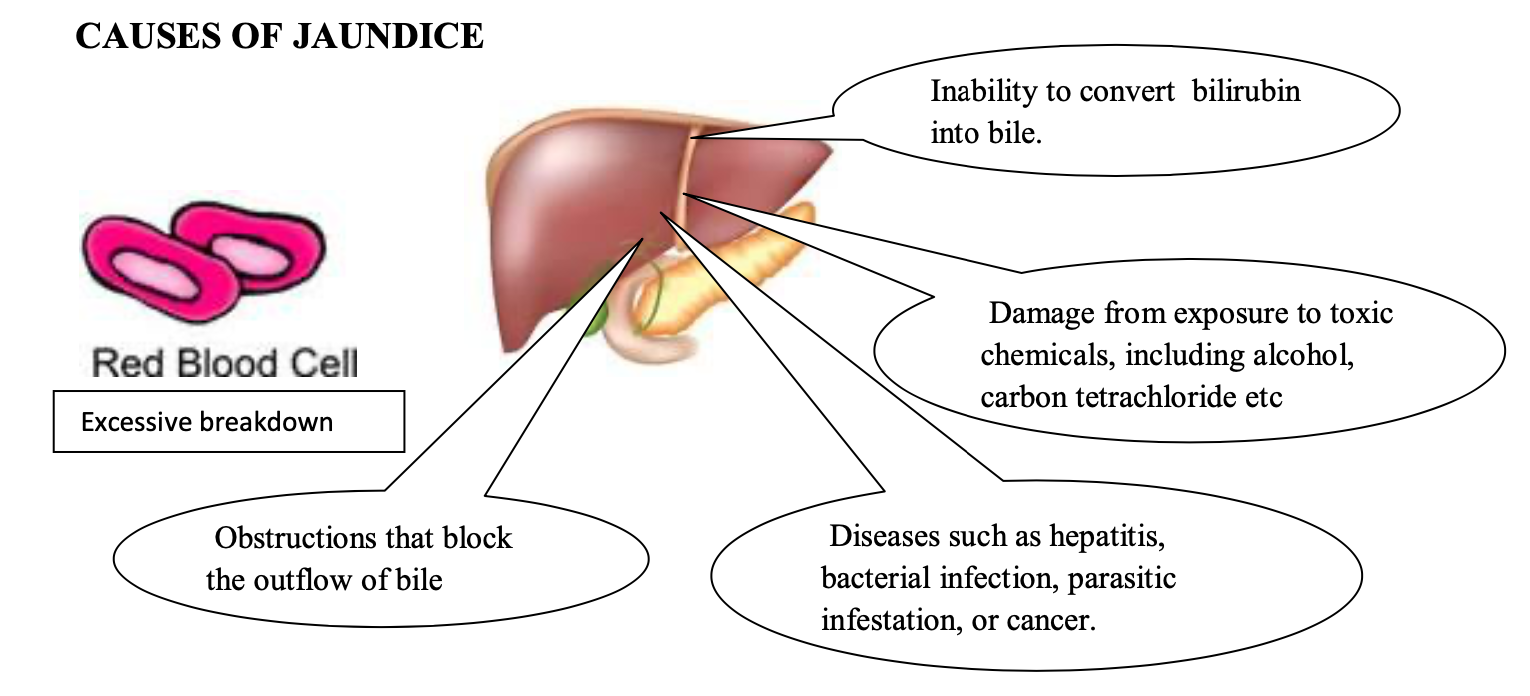
The liver makes bilirubin from dying red blood cells and other sources. It then converts bilirubin into bile, which has several purposes, among them the digestion of fatty acids and neutralization of stomach acid. If there is too much bilirubin for the liver to deal with, or if the liver's functioning is compromised, jaundice can result. The major categories of problems that can lead to jaundice include -
Newborns often develop some degree of jaundice in the days after birth, as their bodies adjust to life outside the womb, but this is not usually a serious problem. Symptoms- There is discoloration of skin, accompanied by itching, which can be intense, as well as by nausea, vomiting, headache, fever, dark-colored urine, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, abdominal swelling, and light-colored stools. |
DIARRHEA
|
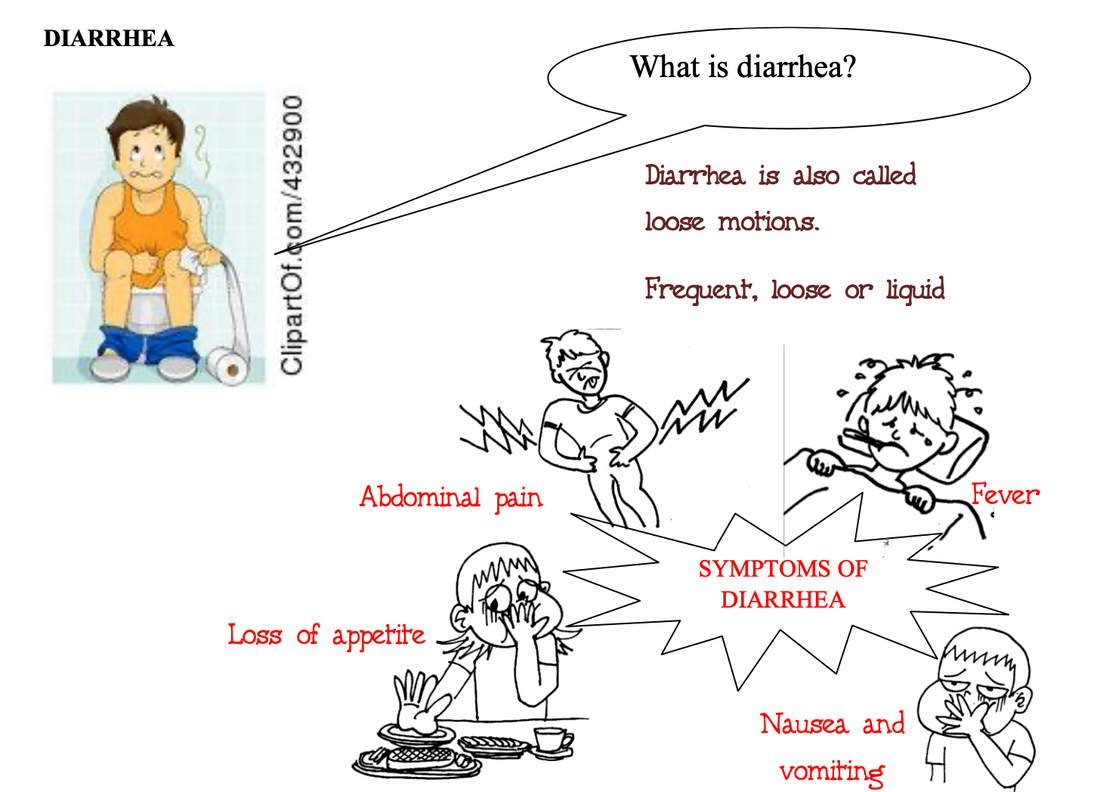
Diarrhea ia also called loose motions. Diarrhoea is not itself a disease, but can be a symptom of several disease. Diarrhoea means there are frequent, loose or liquid stools.
Diarrhea causes dehydration. Children are more likely than adults to die from diarrhoea because they become dehydrated more quickly. Diarrhoea is also a major cause of child malnutrition. Symptoms of diarrhea
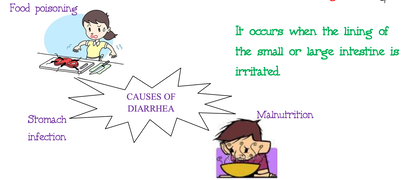
The causes of diarrhoea are many. Out of which the main causes are : Bacterial Infections: Several types of bacteria which get into our body through contaminated food or water, are the main causes of diarrhea. Viral infections . Many viruses are also responsible for the cause diarrhea, including rotavirus, Norwalk virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, and viral hepatitis. Parasitic infections are also a cause for diarrhoea. Food Intolerance - Some people are not able to digest some component of food properly, such as lactose, the sugar found in milk - which ultimately leads to diarrhoea. |
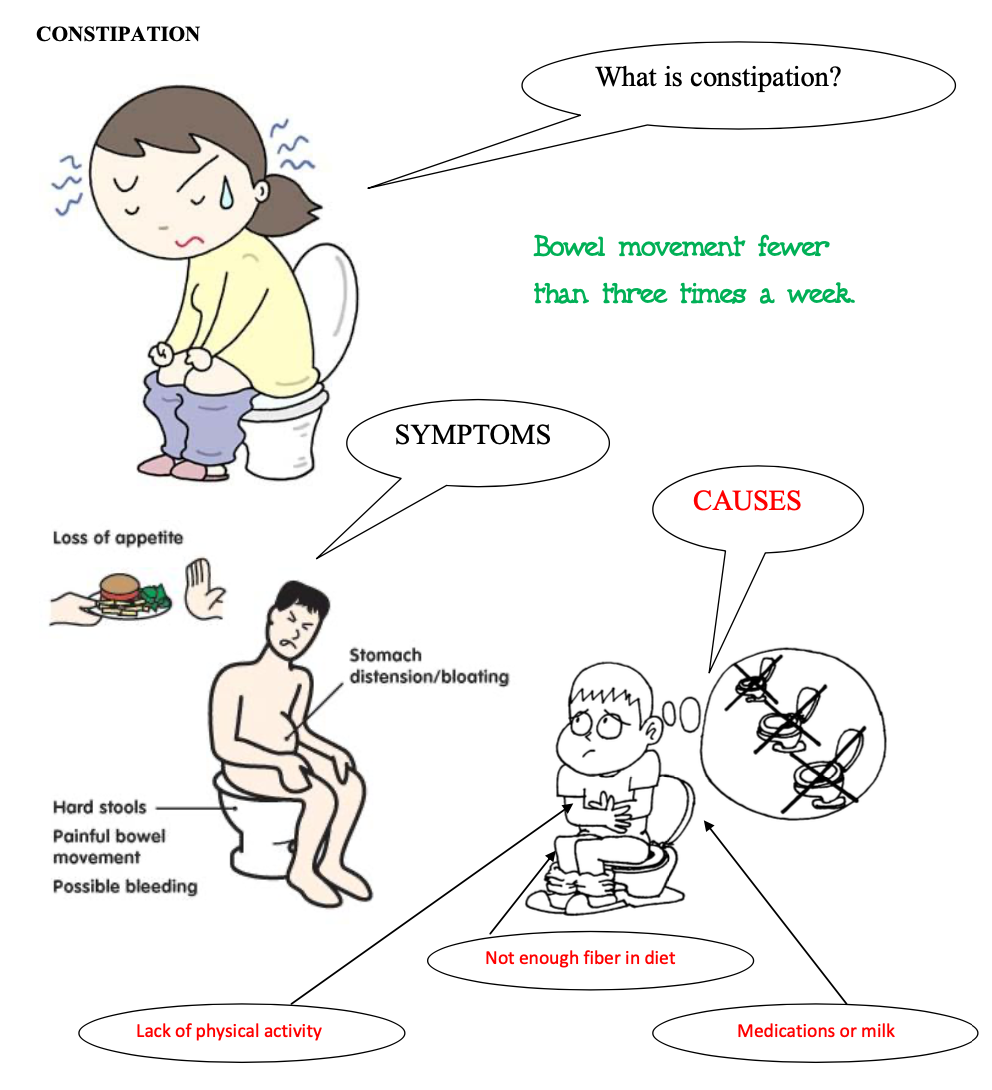
CONSTIPATION
|
Constipation is defined as having a bowel movement fewer than three times per week. With constipation stools are usually hard, dry, small in size, and difficult to eliminate. Some people who are constipated find it painful to have a bowel movement and often experience straining, bloating, and the sensation of a full bowel.
Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences constipation at some point in their life, and a poor diet typically is the cause. Most constipation is temporary and not serious. causes of constipation Constipation occurs when the colon absorbs too much water or if the colon’s muscle contractions are slow or sluggish, causing the stool to move through the colon too slowly. As a result, stools can become hard and dry. Common causes of constipation are
|
|
Vomiting and nausea are not illnesses but common symptoms that accompany with many diseases and conditions. The problems with nausea and vomiting are related to the cause.
Nausea and vomiting from motion sickness, seasickness, food poisoning, or cancer therapy can result in loss of water and electrolytes, which can lead to dehydration. Vomiting and nausea known as morning sickness may occur during pregnancy. Nausea is an unpleasant, queasy feeling in the throat or stomach that may result in vomiting. Vomiting is emptying the stomach as a result of strong gagging and retching that leads to throwing up. The stomach's contents are forcefully expelled through the mouth. Nausea and vomiting are controlled by the same parts of the brain that control involuntary bodily functions. Vomiting is actually a reflex triggered by a signal from the brain. The signal to vomit can result from several stimuli such as smells, taste, various illnesses, emotions (such as fear), pain, injury, infection, food irritation, dizziness, motion, and other changes in the body. The following are common causes of nausea and vomiting.
|
|
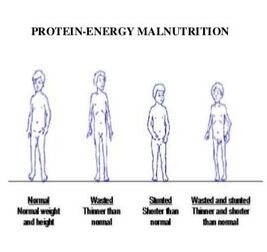
PROTEIN ENERGY MALNUTRITION
Dietary deficiencies of proteins and total food calories are widespread in many underdeveloped countries of South and South-east Asia, South America, and West and Central Africa. Protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) may affect large sections of the population during drought, famine and political turmoil. PEM affects infants and children to produce Marasmus and Kwashiorkar. |
|
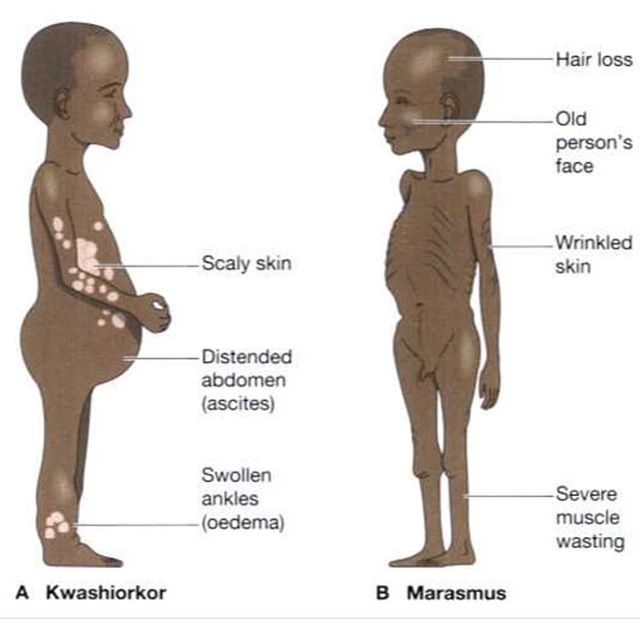
Marasmus is produced by a simultaneous deficiency of proteins and calories.
Kwashiorkar is produced by protein deficiency unaccompanied by calorie deficiency.
|