ISC 12>UNIT 4>HUMAN DISEASES- CAUSATIVE AGENT, SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTION
|
Communicable diseases causative agent, symptoms and prevention of the following:
bacterial diseases (typhoid and pneumonia), viral diseases (common cold, swine flu and dengue), protozoa (malaria and amoebiasis), helminthes (ascariasis and filariasis); Sexually transmitted diseases; (gonorrhoea and syphilis) Non-communicable diseases: Cancer (types, causes, diagnosis and treatment); human genetic disorders: (haemophilia, thalassamia, Down’s syndrome, Klinefeltor’s syndrome and Turner syndrome). Rh factor incompatibility – role of Rh factor in blood transfusion and pregnancy; Genetic counselling- role of genetic counsellors. Organ transplants and brief idea of immuno-supressants. Role of stem cells in medical treatment. |
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
Diseases can be communicable or non communicable.
Communicable diseases are those that are transmitted from one person to the other. These include diseases caused by bacteria, virus, protozoans and helminthes.
Non communicable diseases are those that are not transmitted from one person to the other. These include cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer and genetic disorders.
Communicable diseases are those that are transmitted from one person to the other. These include diseases caused by bacteria, virus, protozoans and helminthes.
Non communicable diseases are those that are not transmitted from one person to the other. These include cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer and genetic disorders.
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
VIRAL DISEASES
1.COMMON COLD
|
Causative agent- Rhinovirus
Symptoms- 1. Nasal stuffiness or drainage 2. Sore or scratchy throat 3. Sneezing 4. Hoarseness, coughing 5. Headache and fever Prevention: Use of- hand sanitizers, disinfectants and facial tissues Treatment: Decongestants for nasal symptoms , Acetaminophen and ibuprofen for headache and fever. |
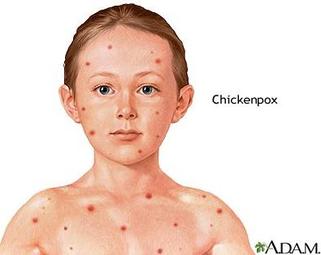
CHICKEN POX
|
Causative agent: Vericella zoster
Symptoms 1.Skin eruptions as red papules 2.Papules grow into pustules. Preventive measures- 1.Patients to be isolated till all scabs fall off. 2.Person attending the patient should clean and wash hands with soap 3.Items used by patient should be cleaned and boiled before reuse 4.Patient should be given antiseptic bath. Treatment: Passive immunity by Zoster Immune Globin |
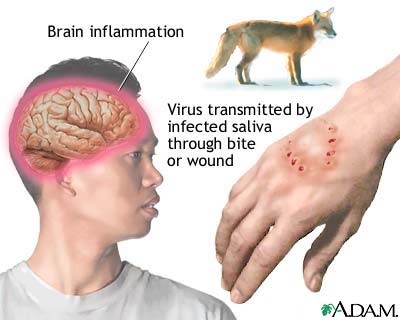
RABIES (HYDROPHOBIA)
|
Causative agent: Street virus
The virus stimulates then destroys the cells of brain and spinal cord. Symptoms 1. Severe headache 2. High fever 3. Painful spasm of muscle and throat. 4. Choking, convulsions and inability to swallow even liquid food. 5. Feels thirsty but has fear of water Prevention 1. Complete immunization of pet dog, cat etc. 2. Isolation or killing of rabied dogs which become mad due to this virus. Treatment: Pasteur treatment |
POLIOMYLETIS
|
Causative agent: Polio virus
Symptoms 1. Affects central nervous system, destroys large motor cells of spinal cord that controls muscular activity. 2. Limbs gets paralysed Prevention- 1. Proper covering of food 2. Avoid eating food items contaminated by flies. Treatment: 1. Poliomyletis vaccine (Salk vaccine) 2. Oral polio vaccine (OPV) http://amhistory.si.edu/polio/activities/lifecycle/lifecycle_10.htm |
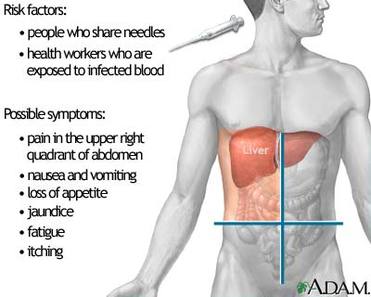
HEPATITIS (Epidemic jaundice)
|
Causative agent: hepatitis virus
Inflammation of liver Symptoms 1. Flue –like symptoms of fever. 2. Yellowing of skin and sclera 3. Headache, joint pains. 4. Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting 5. Irritating rashes Prevention 1. Contamination of water and food 2. Sanitary disposal of excreta 3. Use of boiled or chlorinated water during epidemic Treatment: Attack gives immunity |
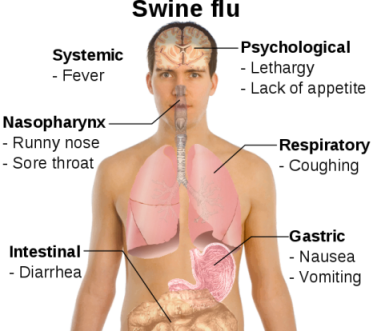
2. H1N1 INFLUENZA (HUMAN SWINE FLU/ SWINE FLU)
3. DENGUE
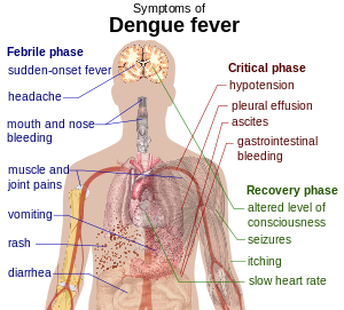
|
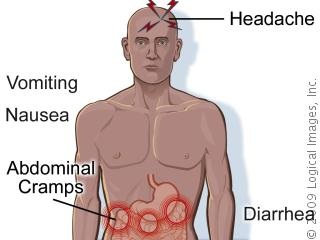
Causative agent: Dengue virus
Transmitted by the bite of an Aedes mosquito Symptoms: (which usually begin four to six days after infection and last for up to 10 days)
Pain in the bone should be treated by analgesics or pain killing tablets. |
BACTERIAL DISEASES
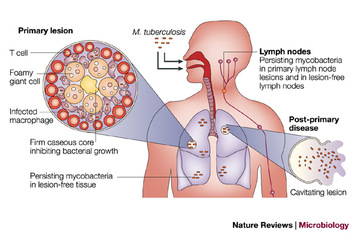
TUBERCULOSIS
|
Causative agent: Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Symptoms 1. Fever 2. General weakness 3. Loss of appetite, persistent coughing 4. Yellowish blood stained sputum Prevention 1. Isolation of TB patients 2. Health education 3. Vaccination by BCG Diagnosed by Mantoux reaction Treatment -Streptomysin, para-amino salicylic acid,rifampicin etc. |
1. TYPHOID
|
Causative agent: Salmonella typhi.
Symptoms 1. Lesions and damage to the intestinal wall. 2. Continued fever. 3. Abdominal tenderness 4. Headache, and slight vomitting Prevention: a. proper community sanitation b. Personal cleanliness c. Protection of food and water dust and flies Treatment Ampicillin and chloromycetin |
CHOLERA
|
Causative agent: Vibrio comma or Vibrio cholerae
Symptoms 1. Acute diarrhoea 2. Vomitting 3. Muscular cramps 4. Stool is white and watery(rice water appearance) Prevention 1. Proper heating of food 2. Boiling of drinking water 3. Proper disposal of wastes 4. Prevent contamination of food by flies Treatment: Replace fluids and electrolytes Tetracycline or other antibiotics |
TETANUS (lock jaw)
|
Causative agent: Clostridium tetani
On entering the body bacteria produce neurotoxin- tetranospasmin Symptoms 1. Painful muscle contractions of neck and jaws. 2. Increased rigidity of jaws-lock jaw 3. Painful arching leading to death Prevention
|
2. PNEUMONIA
|
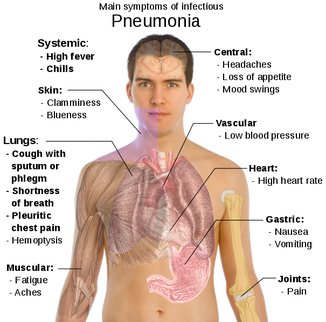
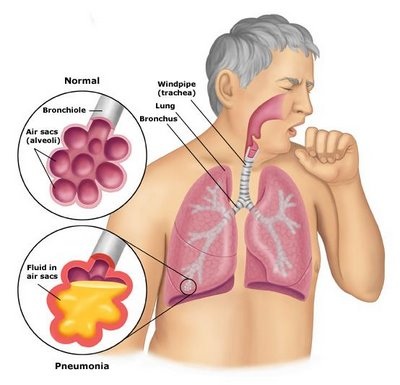
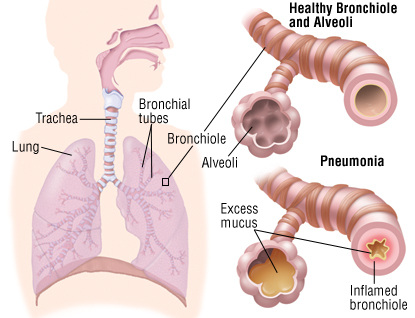
Causative agent- Streptococcus pneumonia
· Infection of lungs · Pneumonia is caused by the inhalation of infected microorganisms (tiny, single-celled living organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or protozoa) spread through contact with an infected person. · The microorganisms enter the body through the mouth, nose and eyes. BACTERIAL PNEUMONIA Pneumonia-causing bacteria is present in many throats, but when the body's defenses are weakened (for example, by illness, old age, malnutrition or impaired immunity) the bacteria can multiply, working its way into the lungs, inflaming the air sacs and filling the lungs with liquid and pus. |
|
VIRAL PNEUMONIA
Half of all pneumonias are believed to be caused by viruses, such as influenza (flu), adenovirus, coxsackievirus, chickenpox, measles, cytomegalovirus and respiratory syncytial virus. These viruses invade the lungs and multiply. Symptoms With viral pneumonia, the person may experience:
|
Treatment
Bacterial pneumonia (caused by the streptococcus pneumonia bacteria) is often treated with penicillin, ampicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin) and erythromycin.
Viral pneumonia does not respond to antibiotic treatment. This type of pneumonia usually resolves over time. If the lungs become infected with a secondary bacterial infection, the doctor will prescribe an appropriate antibiotic to eliminate the bacterial infection.
Prevention
Bacterial pneumonia (caused by the streptococcus pneumonia bacteria) is often treated with penicillin, ampicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin) and erythromycin.
Viral pneumonia does not respond to antibiotic treatment. This type of pneumonia usually resolves over time. If the lungs become infected with a secondary bacterial infection, the doctor will prescribe an appropriate antibiotic to eliminate the bacterial infection.
Prevention
- Practice good hygiene. Get a pneumonococcal vaccine.
- Get a pneumonococcal vaccine.
- Practice good preventive measures by eating a proper diet, getting regular exercise and plenty of sleep.
- Do not smoke.
DISEASES CAUSED BY PROTOZOANS
1. MALARIA
|
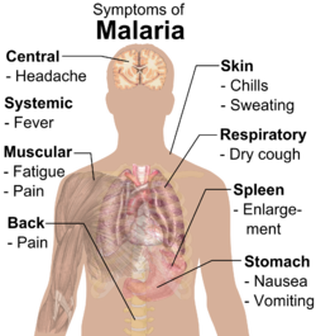
Causative agent: Plasmodium
Transmitted by bite of female Anopheles mosquito Symptoms: 1. High fever with chills 2. Fever subsides with profuse sweating 3. Cycle of fever and sweating repeated after 2-3 days 4. Severe headache 5. Nausea Prevention
SF- 66 vaccine. |
3. AMOEBIASIS
|
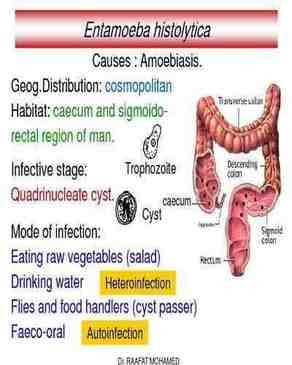
Causative agent: Entamoeba histolytica
Symptoms: 1. Invade intestinal wall, destroy the mucosa. 2. Abdominal pain 3. Nausea 4. Flatulence 5. Bowel irregularity with fatigue and headache. Prevention
|
DISEASES BY HELMINTHES
1. ASCARIASIS
|
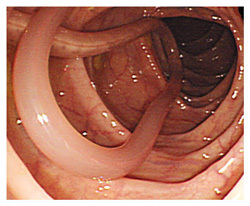
Causative agent: Ascaris lumbricoides
Symptoms: 1. Indigestion 2. Abdominal discomforts 3. Acute colic pain 4. Appendicitis 5. Gastric ulcer with diarrhoea and vomitting. Prevention
|
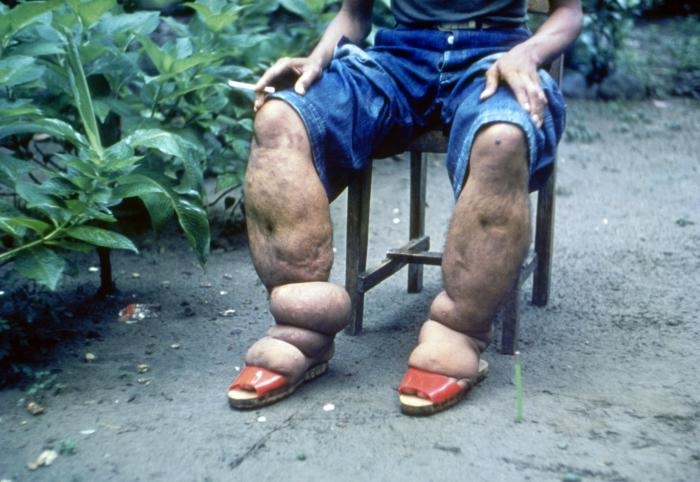
2. FILARIASIS (Elephantiasis)
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are highly infectious, transferred through sexual contact. They are also called general diseases (VD) or reproductive tract infections(RTI).
1.GONORRHOEA
Causative agent: Nisseria gonorrhoea
Symptoms:
1.Infects the mucus membrane of urinogenital tract.
2. genital discharge and painful urination.
Treatment and Prevention:
Effective antibiotics are used for treatment.
Prevention includes- safer sex practices and refraining from sex till the antibiotics are completed.
Symptoms:
1.Infects the mucus membrane of urinogenital tract.
2. genital discharge and painful urination.
Treatment and Prevention:
Effective antibiotics are used for treatment.
Prevention includes- safer sex practices and refraining from sex till the antibiotics are completed.
2. SYPHILIS
Causative agent: Trepanoma pallidium
Symptoms:
1. causes sores and lesions in the genital tract.
2. Burning sensation during urination
3. Later can cause sores in the mouth.
Treatment and Prevention:
Effective antibiotics are used for treatment.
Prevention includes- safer sex practices and refraining from sex till the antibiotics are completed.
Symptoms:
1. causes sores and lesions in the genital tract.
2. Burning sensation during urination
3. Later can cause sores in the mouth.
Treatment and Prevention:
Effective antibiotics are used for treatment.
Prevention includes- safer sex practices and refraining from sex till the antibiotics are completed.
NON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
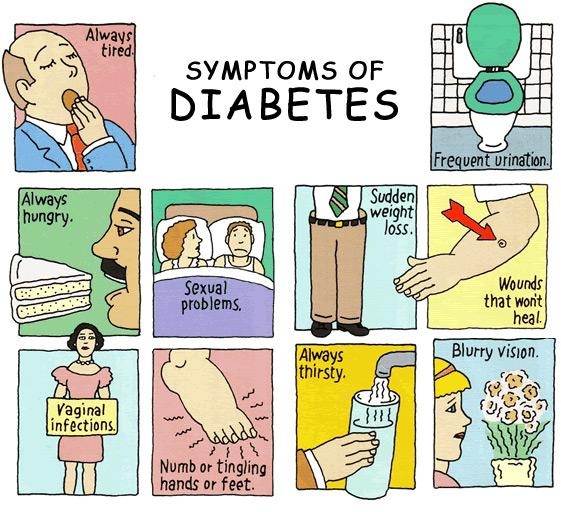
DIABETES MELLITUS
|
Diabetes is a condition of the body where the body is unable to use the sugars from the diet due to malfunctioning of islets of Langerhans of pancreas.
As a result of this sugar accumulates in the blood and tissues causing various defects in the body. Two types – Insulin dependent- deficiency of secreted by islets of Langerhans cells of pancreas. Non- insulin dependent diabetes- failure of target cells to take up insulin from blood Symptoms
Prevention
|
DIABETES MELLITUSCaused due to disturbances in the secretion of insulin from pancreas
There are two types of diabetes mellitus. This concerned with blood sugar balance. Symptoms include excessive urination with sugar in the urine. |
DIABETES INSIPIDUSCaused due to disturbances in secretion of vassopressin by posterior pituitary.
Diabetes insipidus do not have any types. This is concerned with blood water balance. Symptoms include excessive urination, and no sugar in the urine |
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
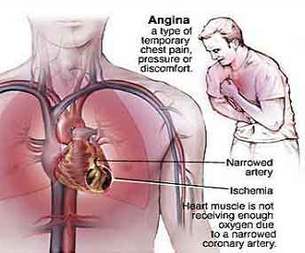
ANGINA PECTORIS
|
When the coronory arteries get blocked, the heart muscles do not get oxygen. This results in sharp pain in the heart and chest. This condition is called angina pectoris.
|
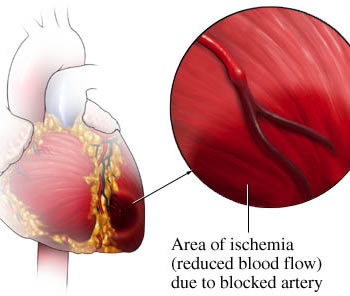
ISCHEMIA/ MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA
|
Cause- heart muscles are damaged or do not work as efficiently due to a reduced blood supply to the heart.
|
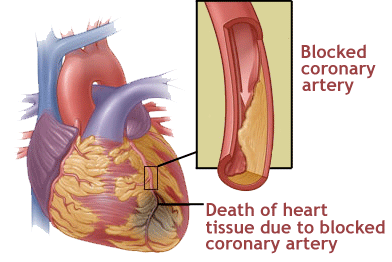
HEART ATTACK
|
A heart attack happens when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a section of heart muscle is suddenly blocked. If blood flow isn't restored quickly, the section of heart muscle begins to die.
May be caused due to different conditions - rheumatic heart disease, atheroma, atherosclerosis, hypertension coronary sclerosis, coronary thrombosis or Ischemia. Symptoms Severe pain in the chest, accompanied by breathlessness, nausea and vomiting. Prevention-
|
Coronary sclerosis
1. Narrowing of coronary artery or its branches due to accumulation of fatty substances.
2. Obstructs blood circulation to the heart causing heart attack. |
Coronary thrombosis
1. Clot is formed in some part of the coronary artery that cuts off the supply of blood to a part of the heart muscles.
2. This is called myocardial infraction. |
Arteriosclerosis
1. Hardening of the arteries. 2. Due to old age arteries harden, because of loss in elasticity or deposition of cholesterol. 3. Causes increased blood pressure leading to rupture of blood vessels of the brain (cerebral haemorrhage) or body (visceral haemorrhage). |
Atherosclerosis
1. Narrowing of arteries
2. Due to deposition of cholesterol on the lining. Causes clot formation or thrombosis. 3. If in coronary artery – heart attack 4. If in brain -- stroke |
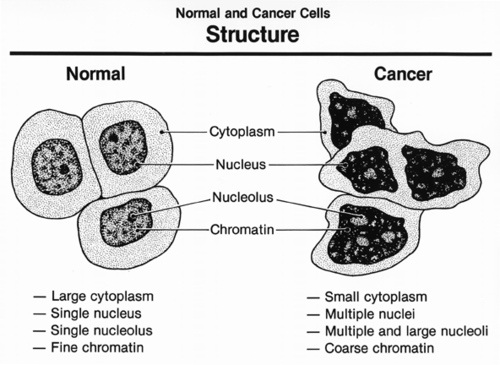
CANCER
|
Uncontrolled growth of a tissue due to unlimited and uncontrolled mitotic divisions.
NEOPLASM- new growth of unwanted cells. TUMOR- undifferentiated lumpy collection of cells. MALIGNANCY- chaotic cells growth that leads into nearby tissues. MALIGNANT- when tumors becomes cancerous. Spread to distant parts is called metastasis. BENIGN- when tumors are non-cancerous DANGER SIGNALS OF CANCER (Diagnostic features): 1. Presence of tumor on lip, tongue or breast. 2. Rapid change in appearance of warts on the body 3. Persistent changes in the bowel movements. 4. Hoarseness in voice, coughing difficulty in swallowing. 5. Continuous bleeding of wound or longer time for healing. 6. Continuous weight loss 7. Uncontrolled mitotic division 8. Cells grow more than normal cells |
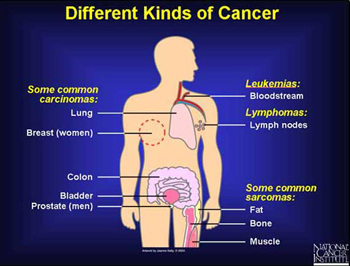
KINDS OF CANCER
CAUSES AND TREATMENT OF CANCER
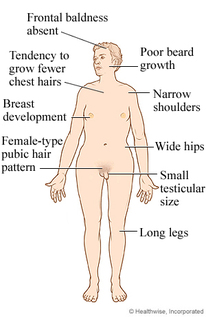
HUMAN GENETIC DISORDERS
|
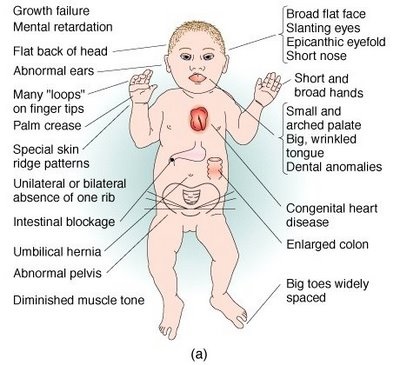
DOWN’S SYNDROME (Mongolian idiocy)
|
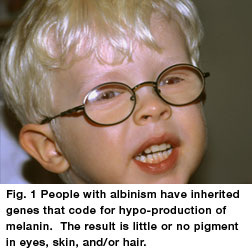
ALBINISM
- Patchy absence of pigment (skin color, patchy) - Lighter than normal skin and hair |
THALASSAEMIA
Rh INCOMPATIBILITY
Develops due to incompatibility of gene
products in the blood. Two well known incompatibilities are ABO blood group and
Rh factor.
ABO incompatibility
Rh factor incompatibility
ABO incompatibility
- With an ABO incompatibility, a mother
makes antibodies against her baby's blood type. It doesn't happen if the mother
and baby have the same blood type or if the baby is type O, since in that case,
there is usually nothing to make antibodies against.
These antibodies, if the mother is type
O, can cross the placenta and can break down the baby's red blood cells after
she is born, leading to jaundice and anemia. This condition is called Hemolytic
Disease of the Newborn or erythroblastosis fetalis, and it can also be caused
by having an Rh incompatibility between a baby and mother.
If a mother is type A or B and the baby
has a different blood type other than type O, she can still make antibodies
against the baby's red blood cells. These antibodies are too large to cross the
placenta though, and so don't usually lead to any problems.
Rh factor incompatibility
- Clinically,
the Rh factor, like ABO factors, can lead to serious medical complications. The
greatest problem with the Rh group is not so much incompatibilities following transfusions (though they can
occur) as those between a mother and her developing fetus. Mother-fetus incompatibility occurs
when the mother is Rh- and her fetus is Rh+ . Maternal antibodies can
cross the placenta and destroy fetal red blood cells.
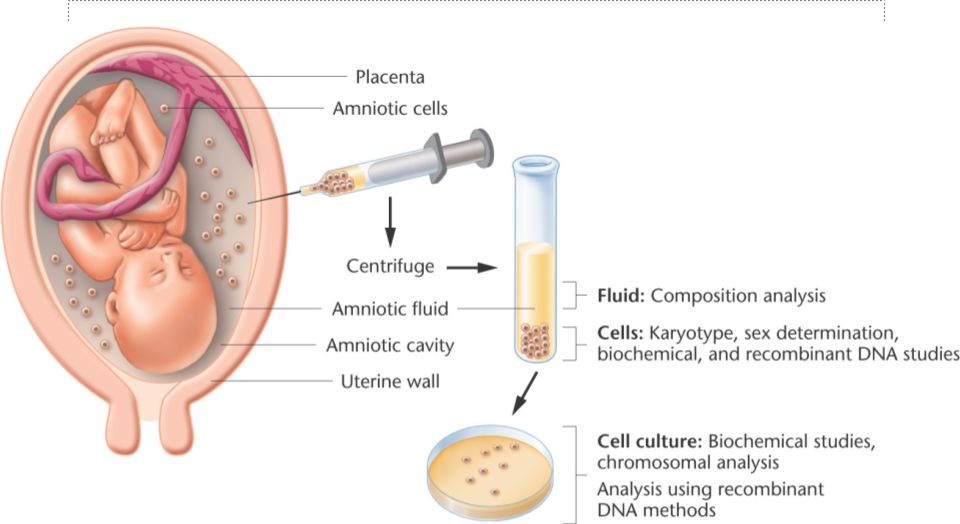
AMNIOCENTESIS
|
Amniocentesis is a procedure used to obtain a small sample of the amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. Amniotic fluid is a clear, pale yellow fluid made by the fetus. The fluid protects the fetus from injury and helps to regulate the temperature of the fetus.
An amniocentesis may be used for genetic and chromosome testing in the second trimester of pregnancy in the presence of one or more of these conditions:
|
GENETIC COUNSELING
(the term was introduced by Sheldon Reed.)
The area of health care that offers advice on genetic problems is called genetic counseling.
It uses different techniques for determination of the actual disease.
Role of genetic counselors.
Educates common man of the dangers of hereditary diseases and various genetic malformations.
Help in educating general public about the use of various information, that is revealed by scientific exploration.
Genetic counselor can predict the characteristics of future generations and can help in planning parenthood.
The geneticist can tell the probability of producing infected offspring by studying pedigree charts of couples.
Suspected errors of metabolism can be identified.
The area of health care that offers advice on genetic problems is called genetic counseling.
It uses different techniques for determination of the actual disease.
Role of genetic counselors.
Educates common man of the dangers of hereditary diseases and various genetic malformations.
Help in educating general public about the use of various information, that is revealed by scientific exploration.
Genetic counselor can predict the characteristics of future generations and can help in planning parenthood.
The geneticist can tell the probability of producing infected offspring by studying pedigree charts of couples.
Suspected errors of metabolism can be identified.